

Talk to the clinician who manages your diabetes before you start a low carbohydrate lifestyle. Low carb lifestyles may not be a good fit for people with certain health conditions or taking certain medications.
Talk to the clinician who manages your diabetes before you start a low carbohydrate meal plan.
Managing your medications
Certain medications should not be used in combination with a low carb meal plan. These include a class of medications called “SGLT2 Inhibitors” which include Jardiance (empagliflozin), Invokana (canagliflozin), Farxiga (dapagliflozin), and Steglatro (ertugliflozin). This also includes combination medications containing an SGLT2 Inhibitor such as SEGLUROMET, XIGDUO, Synjardy, Synjardy XR, Invokamet, Glyxambi, QTERN, and Trijardy XR.
Certain medications often need to be adjusted before you start a low carb meal plan. These include Insulins (such as Humalog, Novolog, Lantus and Basaglar, etc.) and the class of medications called “Sulfonylureas” (such as Amaryl (glimepiride), Glucotrol (glipizide), Diabeta (glyburide), tolbutamide, Tolinase (tolazamide), Diabinese (chlorpropamide), etc).
If you take blood pressure medications, your clinician may need to adjust or stop your medication before you start a low carb eating plan.
We strongly recommend that you have a scheduled visit with your clinician to review your low carb eating plan and your medications before your embark on your JUMPSTART journey.
Keeping You Safe
Talk to your clinician about the symptoms of low blood sugar and low blood pressure and how to treat them as you change your eating plan.
What is a low carb lifestyleWhat is a Low Carbohydrate (Low Carb) Lifestyle or Meal Plan? A low carbohydrate lifestyle or meal plan limits your intake of carbohydrates (carbs) from foods like grains, starchy vegetables, fruit, sugary snacks, and beverages, and emphasizes proteins, non-starchy vegetables, and healthy fats. This generally means eating less than 130g of carbohydrates per day.
?
What is a Low Carbohydrate (Low Carb) Lifestyle or Meal Plan? A low carbohydrate lifestyle or meal plan limits your intake of carbohydrates (carbs) from foods like grains, starchy vegetables, fruit, sugary snacks, and beverages, and emphasizes proteins, non-starchy vegetables, and healthy fats. This generally means eating less than 130g of carbohydrates per day.
What are carbs? Carbs (i.e., carbohydrates) are a nutrient that is broken down by the body into sugar (glucose).
There are 3 types of nutrients: carbs, fat, and protein.
Download a printable version of this page
Very Low Carbohydrate (Ketogenic)
Less than 50 grams of carbs per day
Low Carbohydrate
50-130 grams of carbs per day
Typical American (2,000 calories)
225-325 grams of carbs per day
| 4-5 oz | Grilled Fish or Chicken | 0g carbs |
| 3 cups | Mixed Salad | 5g carbs |
| 1 oz | Feta Cheese and Olives | 1g carbs |
| 2 tbsp | Ranch Dressing | 2g carbs |
| 1/2 | Avocado | 8g carbs |
| 1/2 cup | Brown Rice | 22g carbs |
| 1/2 cup | Black Beans | 22g carbs |
| 4-5 oz | Steak | 0g carbs |
| 1.5 cups | Grilled Vegetables | 10g carbs |

| s slices | Pepperoni Pizza | 70g carbs |
| 4 pcs | Mozzarella Sticks | 30g carbs |
| 1/2 cup | Marinara Sauce | 10g carbs |
| 12 oz | Regular Soda | 40g carbs |
How does a low carb lifestyle help my diabetes?
What is blood sugar (or blood glucose)? Blood sugar is the level of sugar in your blood after your body breaks down nutrients into glucose for energy.
What is insulin? Insulin is a chemical released when you eat carbs. Everyone needs insulin to live.
“The biggest reason I enjoy following low carb meal plan, is that I feel better.... you still get to enjoy good food that is filling.”
Meet Frankie
Frankie was struggling with his weight and managing his diabetes. With an A1C of 11.5 and taking multiple insulin injections a day, he felt miserable and wanted to make a change.
After starting a low carb lifestyle Frankie lost over 100 lbs and stopped taking insulin. Listen to his experience with reducing carbs in this interview.
Benefits of a low carb lifestyle
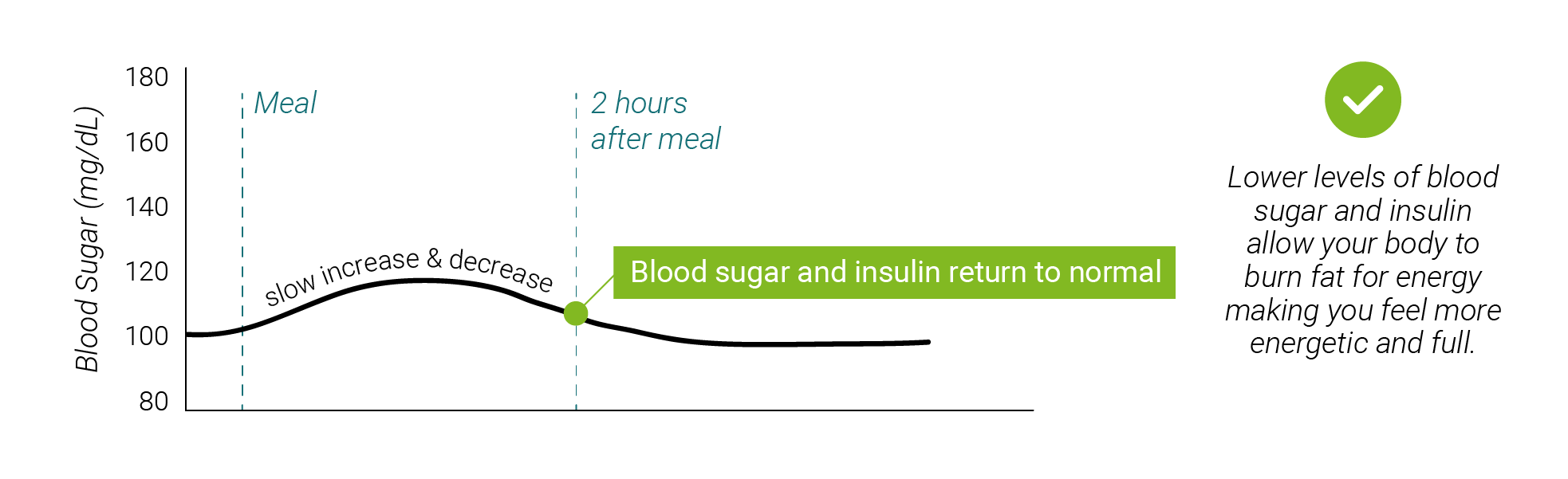
Hover over an icon to learn more about each health benefit.A low carb lifestyle reduces the amount of sugar in your bloodstream, which also lowers your insulin levels. Lower insulin levels allow your body to burn fat for energy and cause you to lose weight over time.
A low carb lifestyle can be effective for lowering your blood pressure. This is likely due to the combined effects of weight loss, reduced insulin levels, and improved kidney function!
A well balanced low carb lifestyle that includes adequate protein, non-starchy vegetables, and fats for flavor. It can help to reduce your hunger, manage cravings and feel full and satisfied for much longer than a high carb meal would.
Reducing the amount of carbs you eat is an effective way to lower your blood sugar. When you eat carbs, they are broken down into sugars during digestion and enter the bloodstream, causing your blood sugars to rise. Eating fewer carbs can help you improve your blood sugar levels by reducing the amount of circulating sugar in the bloodstream.
On a low carb lifestyle, your body adapts to using it’s fat stores and fats from what you eat to provide a steady supply of energy for your body.
What does insulin do?
Insulin helps move glucose (sugar) from the blood into the cells for energy. You can think of insulin as a key that unlocks your cell so that glucose can enter. High levels of insulin tell your body to store extra sugar as fat. Low levels of insulin tell your body to burn fat for energy.

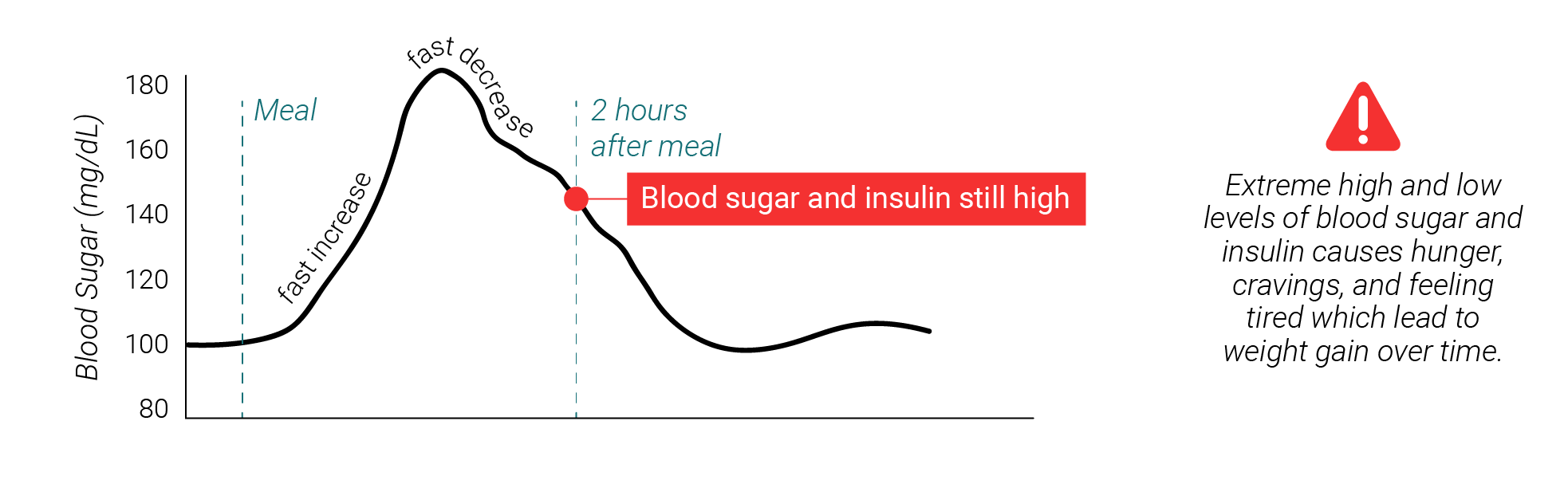
See what happens when you eat a low vs. a high carb meal
Click on a plate to see how much each meal affects your blood sugar
The charts below show how much each meal affects your blood sugar
low carb meal (16g)
high carb meal (150g)
Ready to get started?
Getting started is easy! We recommend 3 simple steps to get started on a low carb lifestyle.
(Remember to talk your doctor before getting started)
1. Start by changing one meal per day (i.e., breakfast). Make changes to your food choices for one meal and do this for a week or two. After you feel comfortable with these changes, consider making changes to a second meal. Focus on...
- Adding protein, non-starchy vegetables, & healthy fats
- Swapping out your starch (bread, rice, potato, pasta etc.) for non-starchy vegetables (broccoli, leafy greens, cauliflower, green beans etc.)
EAT eggs or an omelet
INSTEAD OF cereal, bagel, or toast
2. Replace sugary drinks such as pop and fruit juice with water and unsweetened beverages. Enjoy black coffee and unsweetened teas. If using flavored creamers, replace it with a splash of heavy cream or sugar-free versions.
DRINK tea, fruit-infused water or sparkling water
INSTEAD OF juice or soda
3. Find good snack options. Replace high carb, sugary snacks like chips and baked goods with low sugar fruits like berries. For savory snacks, try veggies and dip, deviled eggs, tuna salad, or nuts and cheese combos. Combining fats and protein help make a balanced and satisfying snack.
LOW CARB SNACK IDEASEAT mixed nuts, string cheese, or jerky
INSTEAD OF packaged snacks
Setting goals and tracking your progress will help you be successful on a low carb lifestyle!
SET GOALS


